Be it muscle pain caused by injuries, headaches caused by Sinusitis, or neck pain caused by simply sleeping wrong, pain is one of the most common health conditions across the globe. In general terms, pain is a feeling of mild or extreme discomfort in the body. It is a signal in the nervous system that might indicate that something is wrong. Pain can be a prick, tingling sensation, soreness, sting, burn, or ache. The intensity of it may vary depending on the cause of the pain.
Different people respond to pain differently – some people have a high tolerance to pain, while others may not. Pain is subjective and its treatment also varies depending on the cause and the severity of it. While some pains can be managed at home through painkillers and home remedies, others may require medical attention. Before we look into how pain can be effectively treated through painkillers, let us understand the possible causes, types, and diagnoses.
What causes pain?
In some cases, the cause of pain is clear, such as an injury to a specific part of the body or a health condition. In other cases, the cause of pain may be vague or unknown. Pain can also be caused due to sleeping in the wrong position, sitting in an awkward or unfavorable position for too long, an accident, or even illnesses such as flu, arthritis, or fibromyalgia. Depending on the illness, you may develop other symptoms – fatigue, nausea, inflammation, and more. Engaging in strenuous physical activities, or lack of the right technique while exercising may also result in severe muscle pain.
However, pain can be treated effectively with accurate diagnosis and specific treatment methods depending on the root cause of the pain. Now, let us take a look at the different types of pain one may encounter during their lifetime.
Types of Pain
Acute pain: Acute pain develops over a short period of time and occurs suddenly, as a result of an injury, illness, or medical procedure. Usually, this type of pain is sharp and goes away within a few days/weeks after the cause has been treated. Almost everyone would have experienced acute pain at some time in their lifetime.
Chronic pain: As the name itself suggests, this type of pain lasts for several months or even years. It usually results from underlying conditions such as arthritis, cancer, fibromyalgia, or migraine. Some people experience chronic pain after a severe injury, even after the injury has been healed.
Nociceptive pain: This type of pain is the result of damaged tissue. It may result from injuries to tissues such as cuts, burns, bruises, or fractures. It can also be caused to health conditions that lead to tissue damage – arthritis, osteoporosis, or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Neuropathic pain: This pain results from nerve damage, which may be caused by an injury, or illness such as slip disc, shingles, diabetes, and more. You may experience a stabbing/shooting sensation and hypersensitivity to touch, movement, and extreme temperatures.
Functional pain: When the pain is caused by no obvious injury or damage to the body, it is known as functional pain. In most cases, functional pain is chronic, though some people may also experience acute functional pain.
Treating pain:
If the pain is not severe and the root cause is obvious and minor, pain can be managed at home through home remedies and over-the-counter (OTC) medicines. However, if the pain is severe or if you are unable to determine the cause of the pain, it is important to seek medical attention.
When you consult a doctor, he/she may ask you about your symptoms and conduct a physical examination. Depending on your medical history and symptoms, he/she may recommend one or more diagnostic tests to undermine the cause, including:
- Blood tests
- Urine tests
- Endoscopy
- X-ray
- CT scan/MRI Scan/Ultrasound scan
- Biopsy
After the root cause has been determined, the doctor will prescribe the right treatment method.
As mentioned earlier, if the pain is mild in nature, it can be treated through home remedies and OTC medications. Some common home treatments include:
- Heat and cold therapy
- Essential oils
- Topical pain relief treatments
- Massage therapy
- Physical therapy
- Pain relief pills
Treating Pain through Topical Pain Relief Techniques:
If you are suffering from painful muscles and joints due to an injury or illness, using a topical pain relief gel or spray is an effective way to obtain relief. Topical painkillers, also known as analgesics, are sprayed on or rubbed into the skin over painful joints or muscles for relief. Although all topical treatments are designed to provide relief from pain, different products use different ingredients or a combination of ingredients to treat the condition. Most topical pain relief solutions contain ingredients such as:
Menthol, methyl salicylate, and camphor – known as counterirritants, as they produce a burning or cooling sensation that distracts you from the pain.
Salicylates – These ingredients offer pain relief and are also found in medicines such as aspirin. They provide a relieving sensation when absorbed into the skin.
Capsaicin – This is one of the most effective ingredients for pain relief. It mostly helps treat joint pain and diabetic nerve pain. When applied, this ingredient causes a warm tingling or burning sensation, which slowly fades over time.
How do topical pain relief solutions work?
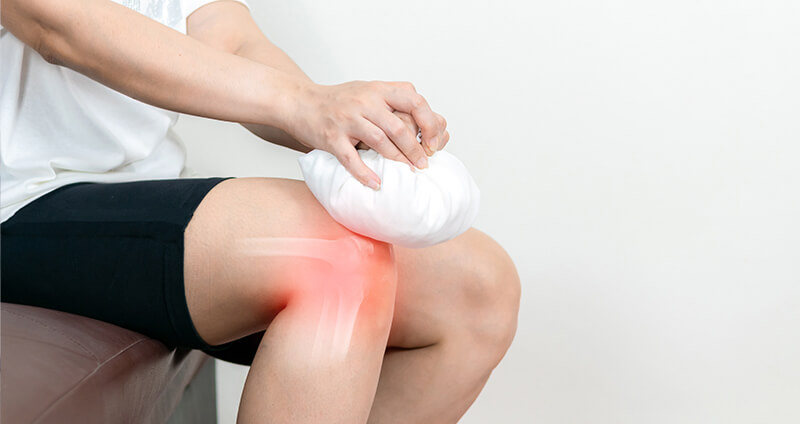
Topical pain relief products such as the Omnigel ointment or pain relief gel work by creating a warm, soothing sensation. They also get easily absorbed into the skin and reach the site of inflammation, thus addressing the root cause of the pain. All pain relief gels contain an active ingredient that helps provide immense relief in a quick manner. Omnigel is an effective pain-killer gel that contains the active ingredient – Diclofenac, which is known for its anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties, and it works by providing relief from pain and reducing inflammation.
How to apply topical painkiller treatments for maximum relief?
Before you apply the pain relief gel, make sure that you read the package insert and look out for warnings. You must also keep in mind that pain relief gels cannot be used on open wounds or damaged skin. Also, you must go through the label the back of the packaging to ensure that there are no ingredients that you are allergic to or prohibited to use by your doctor.In order to obtain maximum relief from pain relief gels, apply sufficient quantity of the gel on the affected area with your fingertips and massage it gently into the skin. Apply it as per the instructions on the package, or as instructed by your doctor.